Musculoskeletal surgery, also known as orthopaedic surgery, is a branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, and prevention of diseases, injuries, and disorders affecting the bones, joints, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves.
Arthroscopy, also known as joint endoscopy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure most used to diagnose and treat joint problems—such as those affecting the knee, shoulder, hip, or ankle.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the skin through which an endoscope is inserted. Using a camera attached to the endoscope, the surgeon obtains a clear view of the inside of the joint and its condition. This allows for the identification, diagnosis, and if necessary, immediate treatment of various abnormalities.
Although arthroscopy is less invasive than open surgery, it is still a significant procedure that typically results in faster recovery and less pain for the patient.
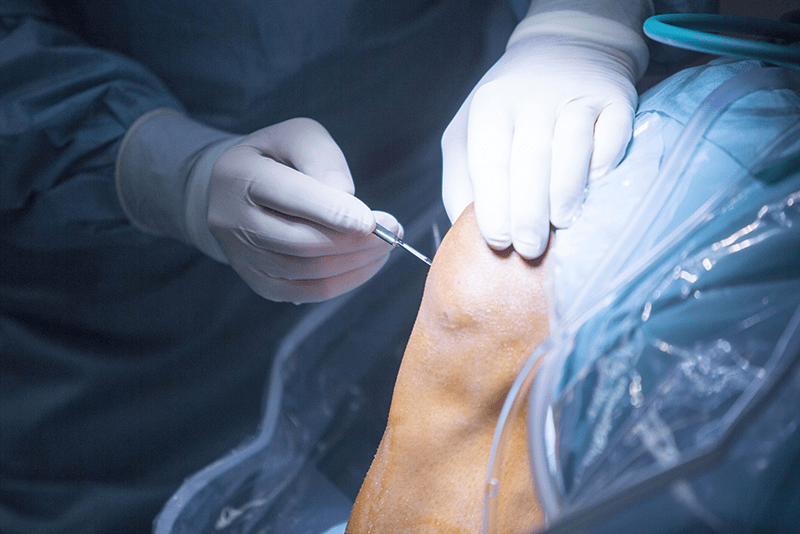
Meniscus arthroscopy is a surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat injuries to the meniscus in the knee joint. The menisci are two C-shaped cartilage structures in the knee that provide stability and weight distribution. This procedure offers benefits such as reduced surgical trauma, faster recovery, and less pain compared to open surgeries. Meniscus arthroscopy is an effective way to treat knee injuries, particularly when conservative treatments, such as rest, physiotherapy, or injections, have not succeeded.
Arthroscopic mosaicplasty is a specialized procedure for restoring cartilage surfaces in the knee (or other joints). The goal is to restore joint function and reduce pain by creating a healthy cartilage surface. The surgeon removes small cylindrical cartilage and bone grafts from other parts of the joint and transplants them onto damaged areas, in a mosaic-like pattern. Mosaicplasty offers effective cartilage restoration, pain reduction, and improved joint function with minimized surgical trauma. Recovery may take weeks or months and often includes physiotherapy.
Arthroscopic shaver cartilage surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat damaged or worn cartilage in the knee joint (or other joints). The "shaver" is a specialized tool that removes loose or damaged cartilage while promoting cartilage regeneration. This procedure is an effective method for treating joint issues, especially when other treatments have not provided satisfactory results.
Arthroscopic loose body removal is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove loose bodies from joints, commonly in the knee, but also in the hip, shoulder, or ankle. These loose fragments of cartilage, bone, or joint tissue can be caused by injury, degenerative disease (e.g., arthritis), or inflammation. This procedure is an effective solution for patients whose loose bodies cause severe joint problems that have not responded to conservative treatments.
Arthroscopic shoulder surgery is a minimally invasive procedure for treating various shoulder issues. The complex structure of the shoulder joint is prone to problems from injuries, inflammation, or degenerative changes. This arthroscopic approach allows surgeons to examine and treat the shoulder joint through small incisions, offering benefits such as less surgical trauma, faster recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring compared to open surgeries. Recovery time depends on the type of intervention and the patient’s condition, with physiotherapy often being key to full recovery.
Bunion surgery is a surgical procedure used to treat a deformity that develops at the base of the big toe, known as a bunion. A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe, often causing pain, inflammation, and misalignment of the toe. The goal of bunion surgery is to relieve pain, correct the toe alignment, and restore normal foot function. Depending on the severity of the bunion and the degree of deformity, several surgical techniques may be used. After the procedure, patients typically wear a special shoe with a stiff sole to protect the foot and aid the healing process. Full recovery usually takes 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s condition. Physical therapy is often necessary to restore mobility and strength in the foot. Bunion surgery offers an effective solution for those suffering from severe pain and deformity when conservative treatments have failed.
Hammertoe is a foot deformity that typically affects the second, third, or fourth toe. In this condition, the middle joint of the affected toe becomes permanently bent, causing pain, skin irritation, and difficulty walking. When conservative treatments—such as wearing properly fitting shoes, using orthotic insoles, or undergoing physical therapy—fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Hammertoe surgery can help eliminate pain and correct the deformity, restoring the toe’s normal function and appearance.
ACL reconstruction, also known as anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery, is a commonly performed procedure used to treat injuries of the ACL—a key stabilizing ligament in the knee that connects the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone). ACL injuries often occur during sports activities due to sudden changes in direction, abrupt stops, or excessive stretching. A torn ACL can cause significant instability in the knee, making it difficult to walk normally, participate in sports, or perform other physical activities. The goal of the surgery is to reconstruct the ligament, restore knee stability, and prevent further injuries, such as damage to the meniscus. ACL reconstruction is a well-established procedure that can effectively restore knee function and stability, especially in active individuals and athletes. Successful recovery depends on proper rehabilitation and a gradual return to normal activities.
The Broström-Gould procedure is a specialized surgical technique used to treat chronic instability of the lateral ankle ligaments. It is primarily recommended for patients who experience frequent ankle sprains or instability and have not responded well to conservative treatments such as physical therapy or the use of orthotic supports. During the Broström portion of the procedure, the surgeon tightens and reattaches the stretched or torn ligaments to their original anatomical position using sutures, thereby restoring the stability of the ankle joint. The Gould modification enhances this repair by reinforcing the ligaments with nearby tendon and tissue structures, providing an additional layer of internal support. The Broström-Gould surgery offers an effective solution for chronic ankle instability, especially in cases where non-surgical approaches have failed to provide relief.
Tarsal tunnel syndrome (TTS) is caused by compression of the tibial nerve and its branches, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the foot and ankle. The goal of tarsal tunnel release surgery is to relieve pressure on the nerve and reduce these symptoms. During the procedure, the surgeon releases the compressed nerve by carefully freeing it from surrounding structures to restore blood flow and nerve function. Tarsal tunnel release surgery can effectively alleviate or eliminate the symptoms of TTS, especially when the condition is diagnosed and treated in its early stages.
Knee and ankle arthroscopy are minimally invasive surgical procedures used to diagnose and treat joint problems. These surgeries are performed using an arthroscope—a small camera inserted into the joint through a tiny incision. This technique provides the surgeon with a detailed view of the inside of the joint and allows for various surgical interventions, such as the removal or repair of damaged tissue, to be carried out if necessary. Arthroscopy is an effective way to address joint issues while minimizing surgical risks and reducing recovery time.
Knee arthroscopic cartilage repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat cartilage damage in the knee joint. This procedure involves examining the knee and repairing or replacing the damaged cartilage using an arthroscope—a small camera inserted through a tiny incision in the knee joint. This allows the surgeon to visualize and treat the cartilage injury directly. Knee arthroscopic cartilage repair can be an effective treatment, especially for patients with early-stage cartilage damage. With proper rehabilitation and medical care, most patients regain knee function and experience significant pain relief.
Our institution’s musculoskeletal surgeon:
Contact us!









